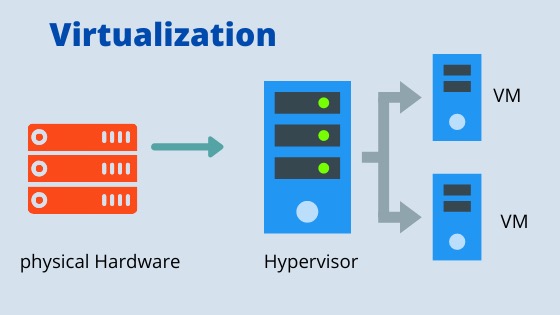
What is Virtualization?
Virtualization is the act of dividing shared computational resources: CPU, RAM, Disk, and Networking into isolated resources that are unaware of the original shared scope.
虚拟化是将共享计算资源:CPU、RAM、磁盘和网络划分为不知道原始共享范围的孤立资源的行为。
What is a virtual machine?
A VM is a virtual env that functions as a virtual computer system with its own CPU, memory, nw interface, & storage, created on a physical hw system (located off- or on-prem). It uses sw instead of a physical computer to run programs & deploy apps.
VM 是一个虚拟环境,它作为一个虚拟计算机系统运行,具有自己的 CPU、内存、nw 接口和存储,在物理硬件系统(位于外部或内部)上创建。 它使用 sw 而不是物理计算机来运行程序和部署应用程序。

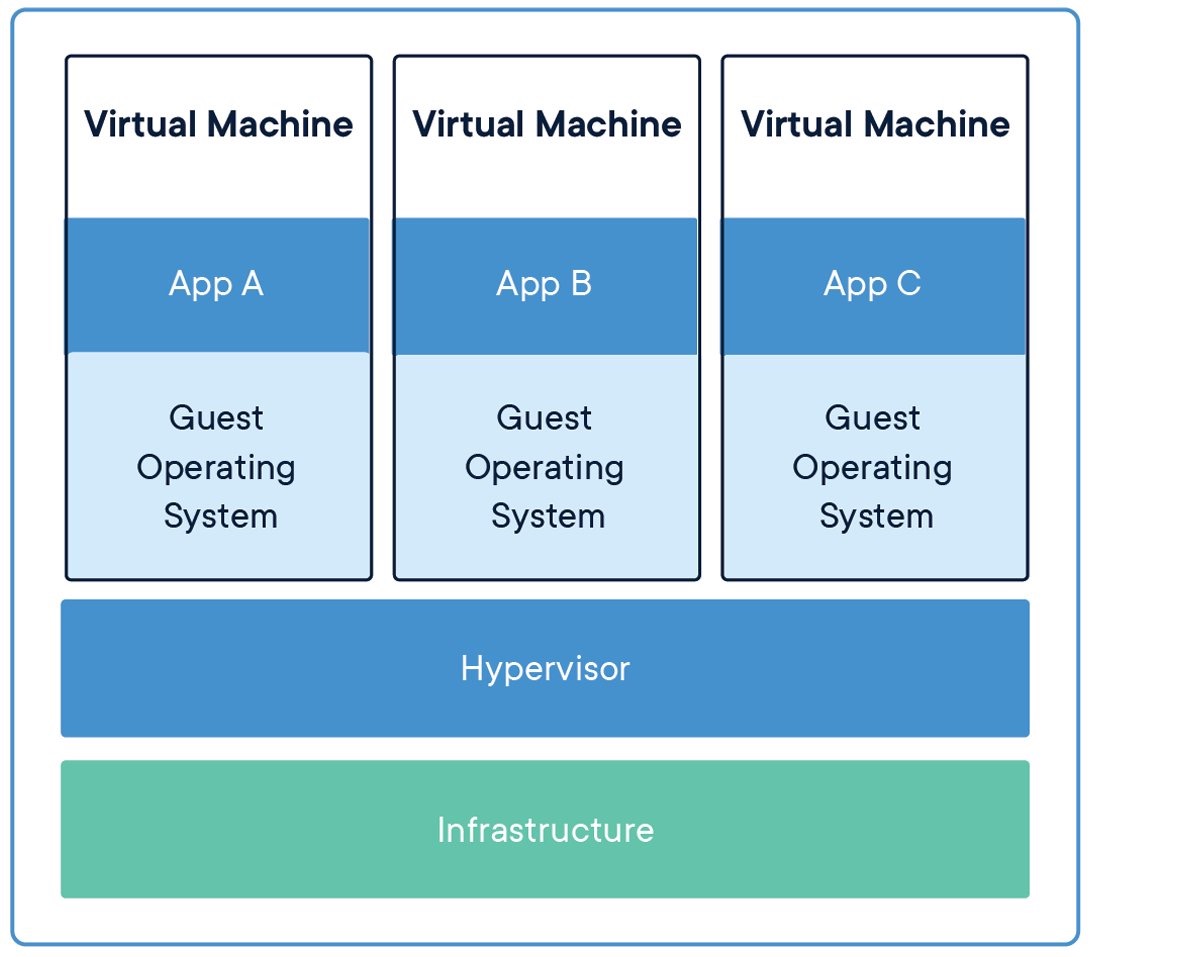
The hypervisor allows multiple VMs to run on a single machine. Each VM includes a full copy of an operating system, the application, necessary binaries and libraries - taking up tens of GBs. VMs can also be slow to boot.
管理程序允许多个 VM 在一台机器上运行。每个 VM 都包含操作系统、应用程序、必要的二进制文件和库的完整副本 - 占用数十 GB。 VM 的启动速度也可能很慢。
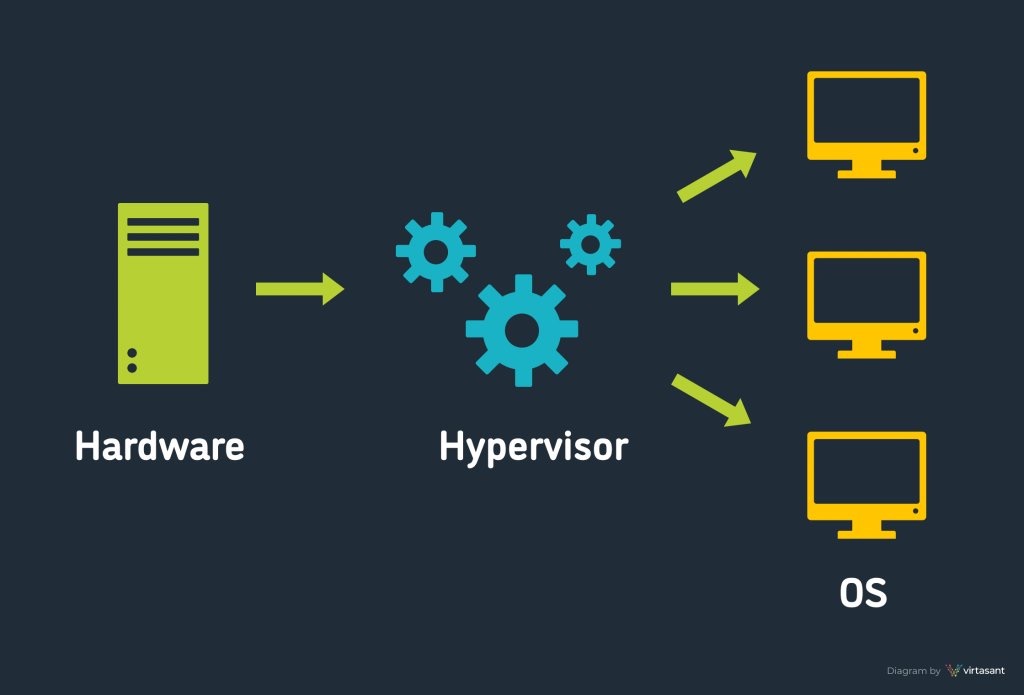
What is a hypervisor?
A hypervisor is software that creates & runs virtual machines (VMs). A hypervisor, sometimes called a virtual machine monitor (VMM), isolates the hypervisor operating system & resources from the virtual machines & enables the creation & mgmt of those VMs.
管理程序是创建和运行虚拟机 (VM) 的软件。管理程序,有时称为虚拟机监视器 (VMM),将管理程序操作系统和资源与虚拟机隔离,并支持创建和管理这些 VM。
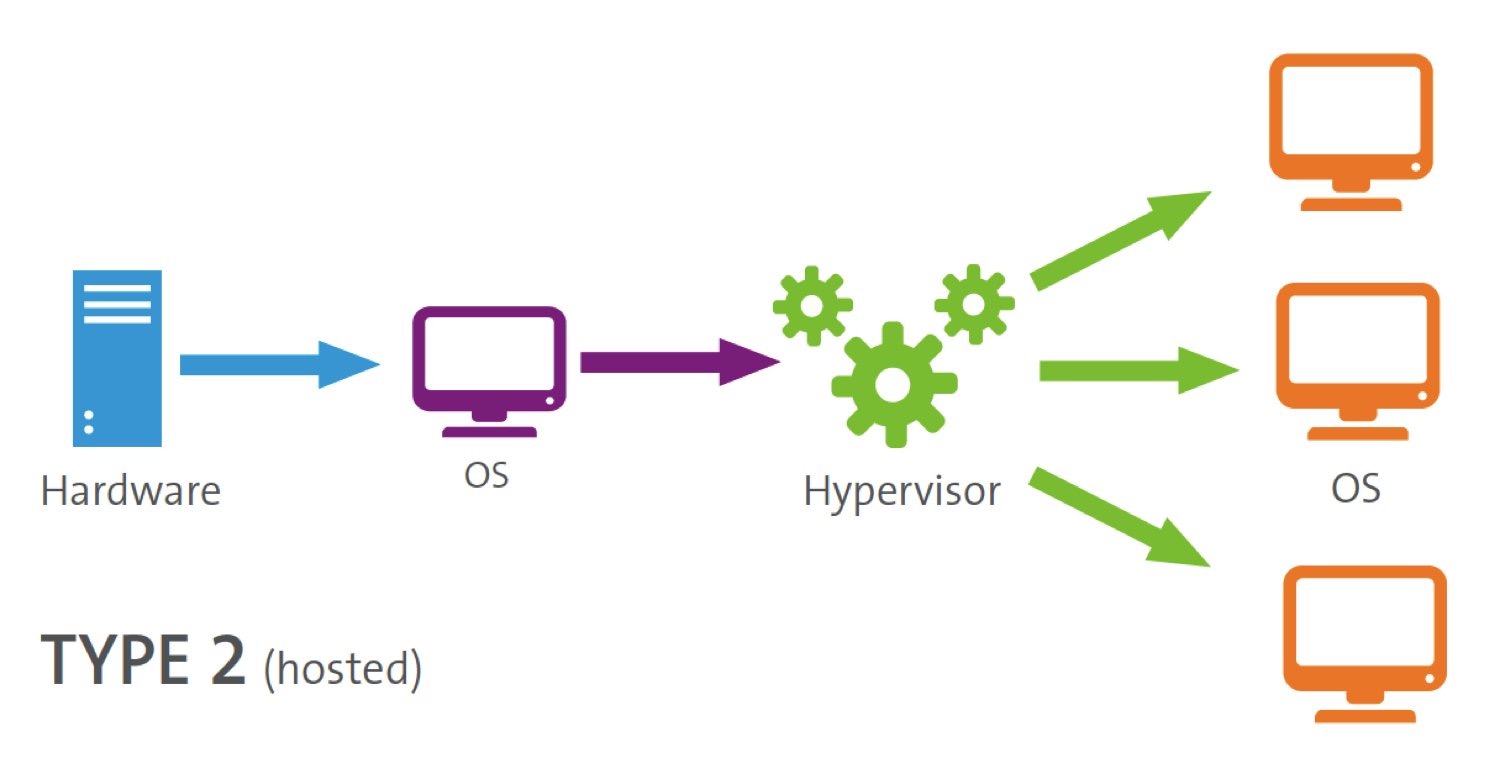
Types of hypervisors
There are 2 different types of hypervisors that can be used for virtualization.
有两种不同类型的管理程序可用于虚拟化。
Type 1 - A type 1 hypervisor is on bare metal. VM resources are scheduled directly to the hardware by the hypervisor. KVM is an example of a type 1 hypervisor. 类型 1 - 1 类虚拟机管理程序位于裸机上。 VM 资源由管理程序直接调度到硬件。 KVM 是类型 1 管理程序的一个示例。

Type 2 - A type 2 hypervisor is hosted. VM resources are scheduled against a host operating system, which is then executed against the hardware. VMware Workstation and Oracle VirtualBox are examples of type 2 hypervisors. 类型 2 - 类型 2 管理程序是托管型。 VM 资源针对主机操作系统进行调度,然后针对硬件执行。 VMware Workstation 和 Oracle VirtualBox 是类型 2 管理程序的示例。
What are Containers?
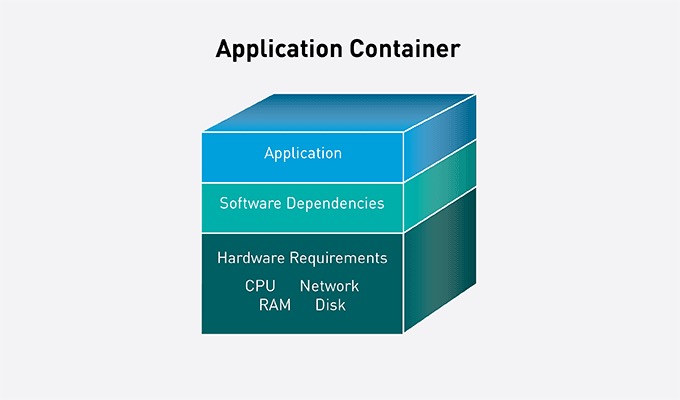
A container is a pkg of sw that includes all dependencies: code, runtime, config, & system libraries so that it can run on any host system. At runtime, the container is also granted its own isolated slice of OS resources like CPU, RAM, Disk, & Networking.
容器是包含所有依赖项的 sw 包:代码、运行时、配置和系统库,以便它可以在任何主机系统上运行。
在运行时,容器还被授予自己独立的操作系统资源片,如 CPU、RAM、磁盘和网络。
Why do you need Containers?
Containers are extremely useful in scaling DevOps efficiency across multiple codebases & developer headcount. Containers ensures that containerized code works consistently on any machine the container is deployed to.
容器在跨多个代码库和开发人员人数扩展 DevOps 效率方面非常有用。容器确保容器化代码在容器部署到的任何机器上一致地工作。
How does a container work?
Containers virtualize a machines operating system at the user space level. Virtualizing user space leverages the existing mechanisms that divide system resources between separate user accounts and programs on an operating system.
容器在用户空间级别虚拟化机器操作系统。虚拟化用户空间利用现有机制在操作系统上的单独用户帐户和程序之间划分系统资源。
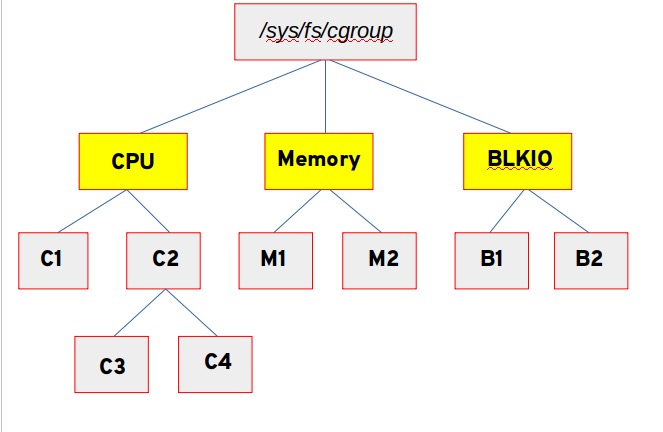
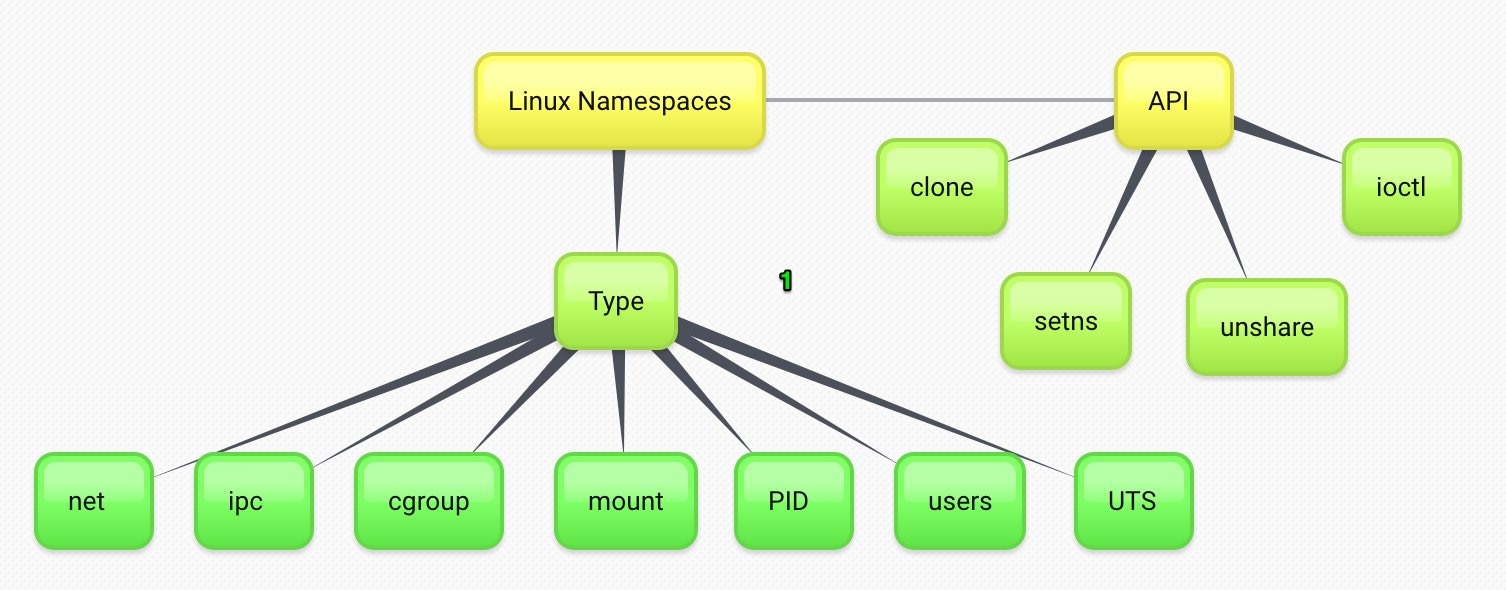
The Linux kernel has a few features that make this possible -> cgroups- It allow processes & their resources to be grouped, isolated, & managed as a unit. Namespaces- limit what processes can see of the rest of the system.
Linux 内核有一些特性使这成为可能 ->
cgroups- 它允许将进程及其资源作为一个单元进行分组、隔离和管理。
命名空间 - 限制哪些进程可以看到系统的其余部分。
Benefits of containers
- Less overhead - Containers require less system resources than traditional or hardware virtual machine environments because they don’t include operating system images. 更少的开销 - 容器比传统或硬件虚拟机环境需要更少的系统资源,因为它们不包含操作系统映像。
- Increased portability - Applications running in containers can be deployed easily to multiple different operating systems and hardware platforms. 增加便携性 - 在容器中运行的应用程序可以轻松部署到多个不同的操作系统和硬件平台。
- More consistent operation - DevOps teams know applications in containers will run the same, regardless of where they are deployed. 更一致的操作 - DevOps 团队知道容器中的应用程序将运行相同,无论它们部署在哪里。
- Greater efficiency - Containers allow applications to be more rapidly deployed, patched, or scaled. 更高的效率 - 容器允许更快速地部署、修补或扩展应用程序。
- Better application development - Containers support agile and DevOps efforts to accelerate development, test, and production cycles 更好的应用开发 —— 容器支持敏捷和 DevOps 工作,以加快开发、测试和生产周期。
Container use cases
Application Modernization
Modernizing applications today means migrating programs from legacy on-premises deployments to cloud solutions. Bcoz containers are agile, they enhance an organization’s ability to migrate applications & workflows seamlessly.
今天的应用程序现代化意味着将程序从传统的本地部署迁移到云解决方案。 Bcoz 容器是敏捷的,它们增强了组织无缝迁移应用程序和工作流的能力。
Refactor existing applications for containers
Although refactoring is much more intensive than lift-and-shift migration, it enables the full benefits of a container environment.
尽管重构比直接迁移要密集得多,但它可以充分发挥容器环境的优势。
Deploying Microservices
The microservices architecture allows sw developers to produce apps made up of several independent deployable services. Different components of d application hosted in containers are scalable & amenable to updating w/o disrupting other services.
微服务架构允许软件开发人员生成由几个独立的可部署服务组成的应用程序。托管在容器中的应用程序的不同组件是可扩展的,并且可以在不中断其他服务的情况下进行更新。
Provide DevOps support for continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD)
Container technology supports streamlined build, test, and deployment from the same container images.
容器技术支持从相同的容器映像简化构建、测试和部署。
Provide easier deployment of repetitive jobs and tasks
Containers are being deployed to support one or more similar processes, which often run in the background, such as ETL functions or batch jobs.
正在部署容器以支持一个或多个类似的流程,这些流程通常在后台运行,例如 ETL 功能或批处理作业。
Containers vs VMs
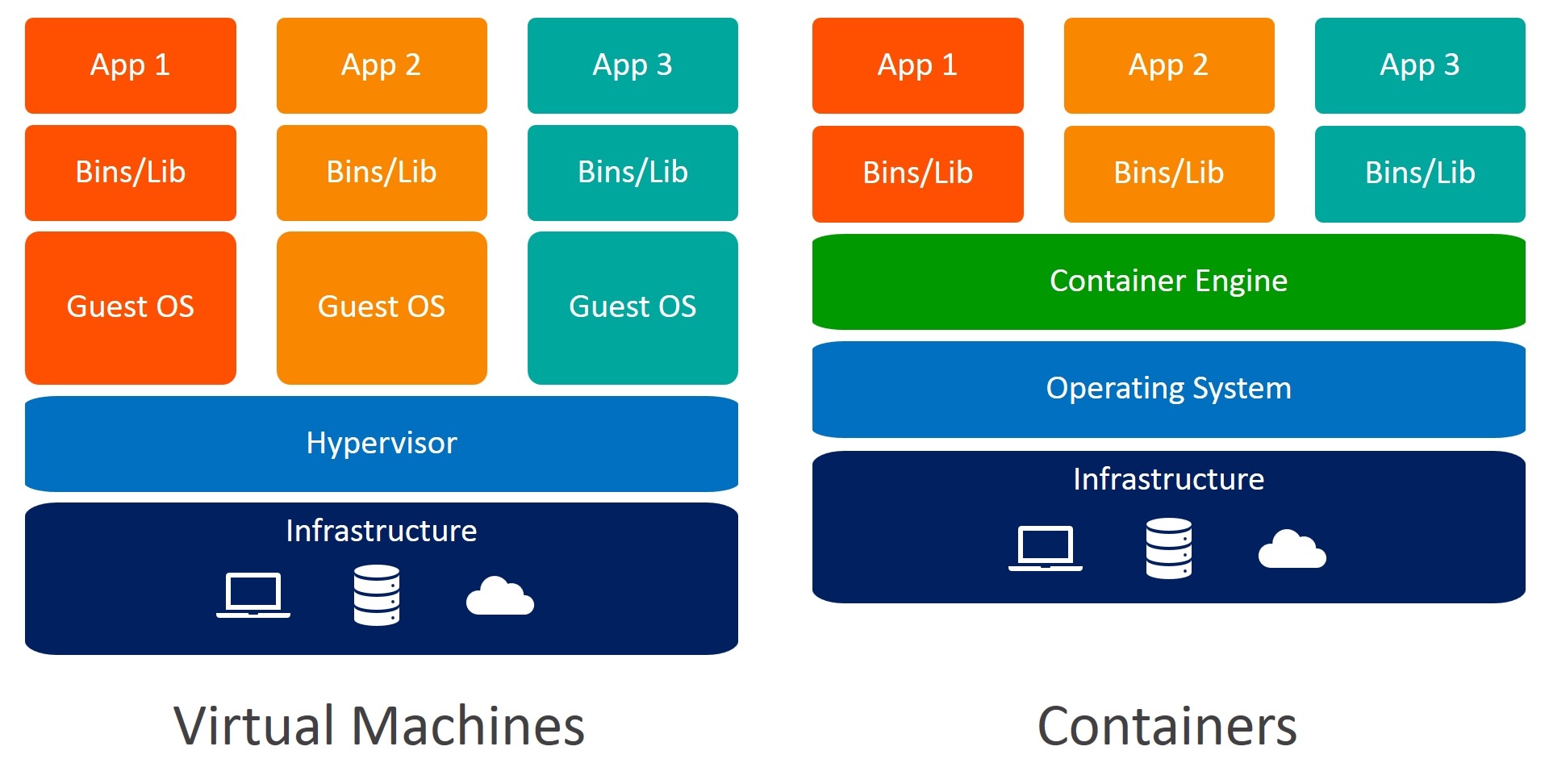
VM’s simulate d entire machine & OS. Means VMs have simulated CPU/RAM/Filesystems/nw resources. Containers only virtualize d user space of an existing OS. Therefore containers r much more lightweight den VMs. Containers can be utilized in an existing host OS.
VM 模拟整个机器和操作系统。意味着 VM 具有模拟的 CPU/RAM/ 文件系统 /nw 资源。
容器仅虚拟化现有操作系统的用户空间。因此,容器是更轻量级的虚拟机。容器可以在现有的主机操作系统中使用。
What are (Kubernetes) Pods?
Pods are the smallest deployable units of computing that you can create & manage in Kubernetes. A Pod is a group of one or more containers, with shared storage & nw resources, & a specification for how to run d containers.
Pod 是您可以在 Kubernetes 中创建和管理的最小的可部署计算单元。
Pod 是一组一个或多个容器,具有共享存储和网络资源,以及如何运行容器的规范。
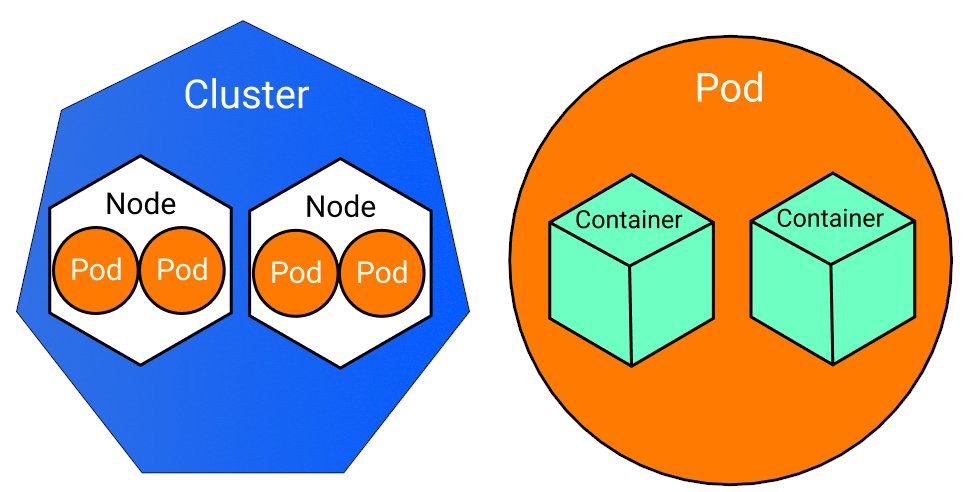
What is a cluster?
A cluster is a board that provides the circuitry to run all the pods (which have the container instances in them) in an orchestrated manner as defined by the users. So there’s a symbiotic relationship between these terms:Container → Pod → Cluster
集群是一块电路板,它提供了以用户定义的编排方式运行所有 pod(其中包含容器实例)的电路。
因此,这些术语之间存在共生关系:容器 → Pod → 集群
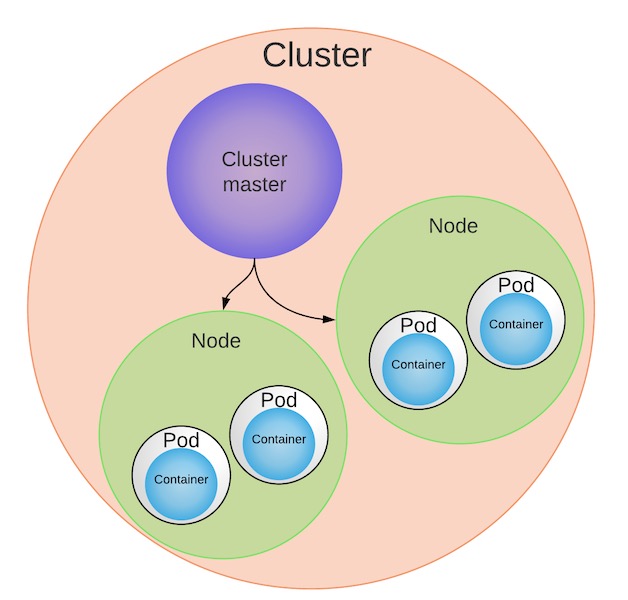
- A container runs logically in a pod (though it also uses a container runtime). 容器在 pod 中逻辑运行(尽管它也使用容器运行时)。
- A group of pods, related or unrelated, run on a cluster. 一组相关或不相关的 Pod 在集群上运行。
- A cluster can contain many pods, related or unrelated [&] grouped under d tight logical borders called namespaces. 一个集群可以包含许多 Pod,相关的或不相关的 [&;] 在称为命名空间的紧密逻辑边界下分组。